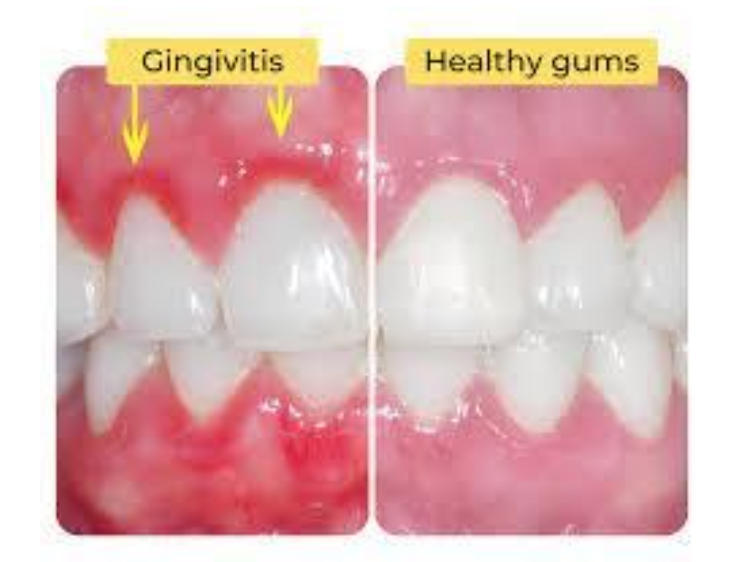
Healthy gum is the foundation of your health
Gum health is often overlooked in discussions about oral hygiene and overall dental care. Many patients focus primarily on avoiding tooth cavities, neglecting the critical role that healthy gums play in maintaining oral health. Gum disease, or periodontal disease, can lead to serious complications if left untreated, including tooth loss and even systemic health issues.
It's essential to recognize that healthy gums serve as a foundation for your teeth, providing necessary support and protection. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are vital for identifying early signs of gum disease, such as inflammation, redness, or bleeding. It plays a significant role in preventing systemic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. To maintain good gum health, practice regular dental hygiene by brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and scheduling routine dental check-ups and cleanings. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, can support gum health. Avoiding tobacco products and managing stress can further enhance your gum health, contributing to a healthier smile and body.
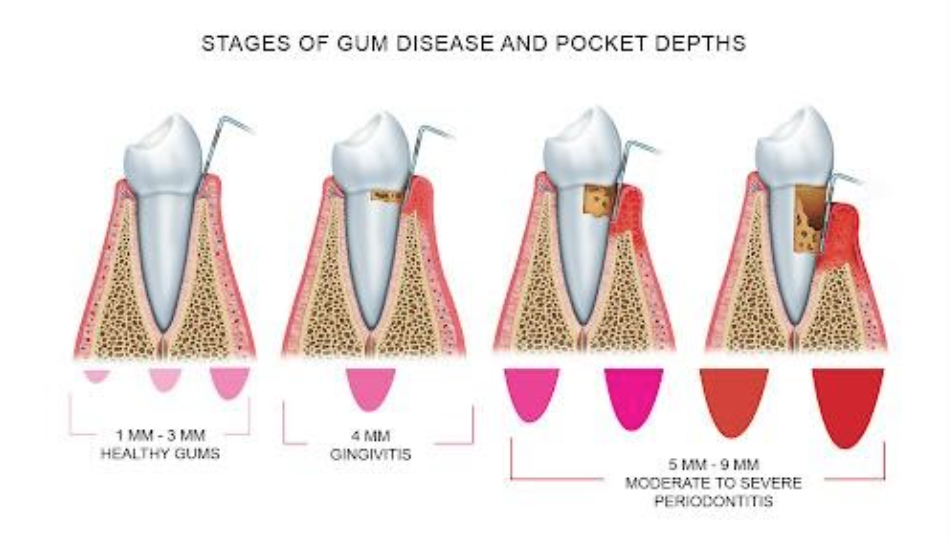
Signs of Gum disease
Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing
Persistent bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
Receding gums or gums that pull away from teeth
Loose or shifting teeth
Pain or discomfort when chewing
Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
Red, swollen, or inflamed gums
Increased sensitivity in teeth
Pus between the teeth and gums
Professional Dental Cleanings
Regular cleanings by a dental professional can help to remove plaque and tartar buildup, preventing further gum disease.
Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
The deep cleaning procedure involves removing bacterial plaque and tartar from below the gum line. Root planing smooths the tooth roots to help gums reattach.
Maintenance Therapy
After initial treatment, regular dental visits and cleanings are essential for maintaining gum health and preventing recurrence.
Laser Therapy
Laser treatments can remove diseased gum tissue and promote healing while minimizing discomfort and recovery time.
Periodontal Surgery
In advanced cases, surgical options such as flap surgery or bone grafting may be necessary to restore tissue and bone around the teeth.
Lifestyle Changes
Improving oral hygiene practices, quitting smoking, and following a balanced diet can significantly support treatment and enhance gum health.